mn create-app example.micronaut.micronautguide --build=gradle --lang=kotlinSecure a Micronaut application with Google
Learn how to create a Micronaut application and secure it with Google and provide authentication with OpenID Connect
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 3.9.2
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Kotlin.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE
-
JDK 1.8 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
4. Writing the Application
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
If you don’t specify the --build argument, Gradle is used as the build tool. If you don’t specify the --lang argument, Java is used as the language.
|
The previous command creates a Micronaut application with the default package example.micronaut in a directory named micronautguide.
4.1. Views
Although the Micronaut framework is primarily designed around message encoding / decoding, there are occasions where it is convenient to render a view on the server side.
To use the Thymeleaf Java template engine to render views in a Micronaut application, add the following dependency on your classpath.
implementation("io.micronaut.views:micronaut-views-thymeleaf")4.2. OAuth 2.0
Visit https://console.developers.google.com and create a new project:
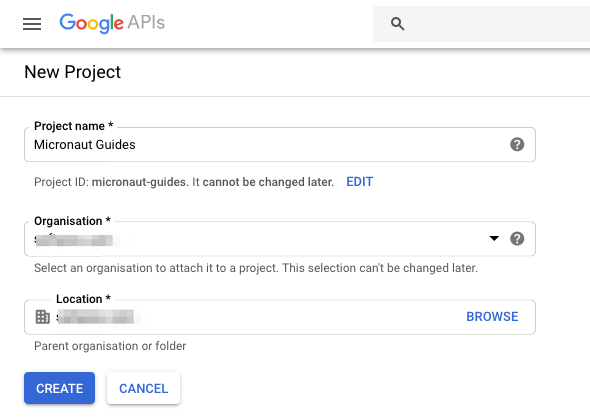
You will also need to create OAuth 2.0 credentials for the project since Google does not do that automatically. From the sidebar, click the Credentials tab, the click Create credentials and choose OAuth client ID from the dropdown.
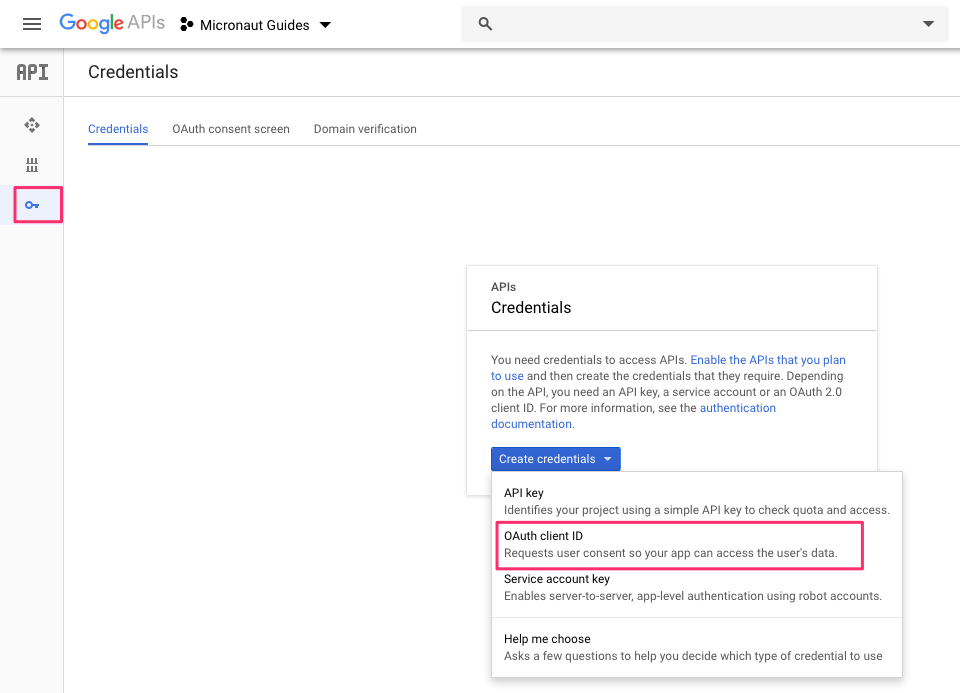
The Google Console will prompt for some information about your application such as the product name, a home page, and a logo. On the next page, select Web Application type, and enter the redirect URL where the Micronaut application we will build next will wait for the callback.
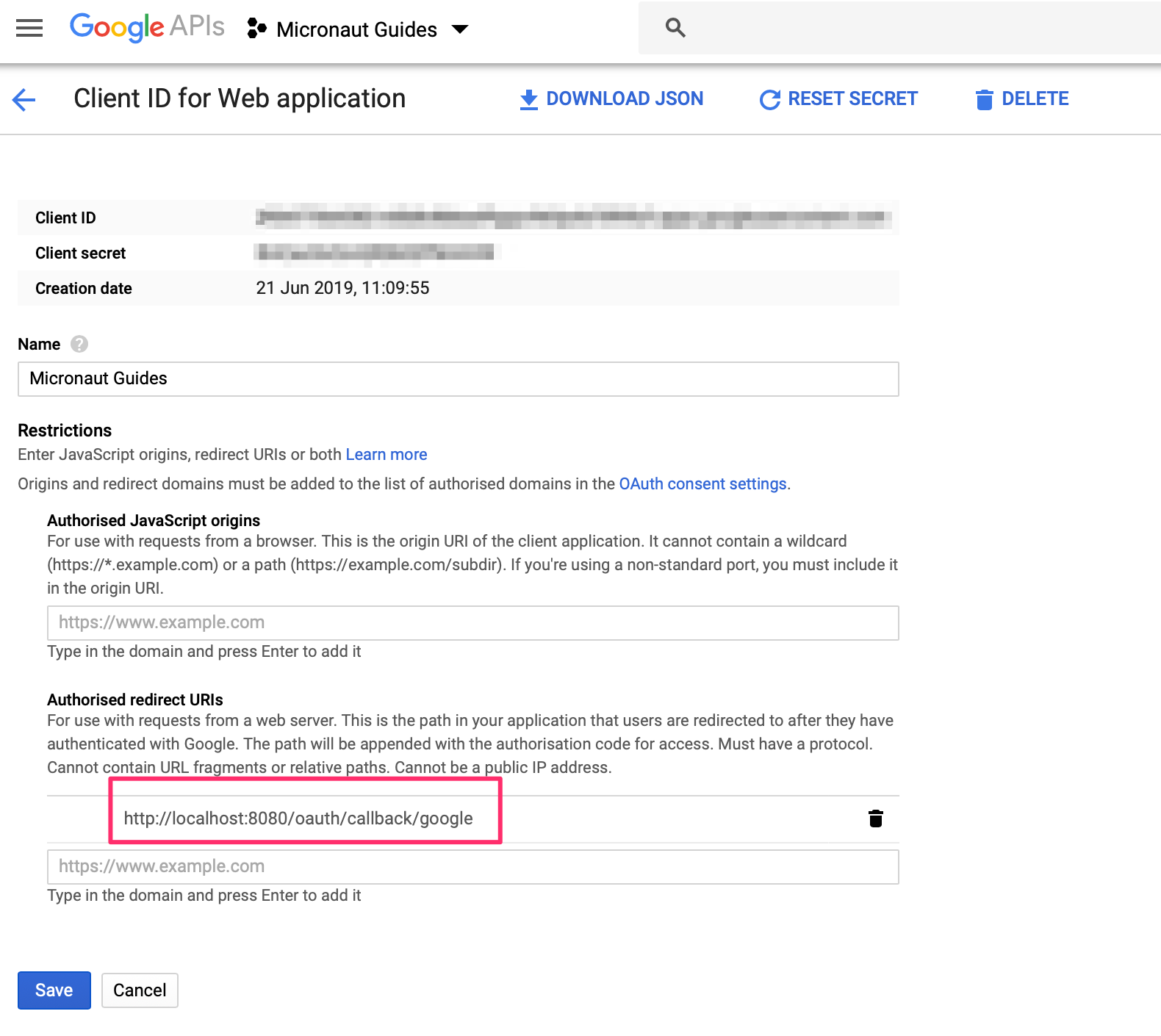
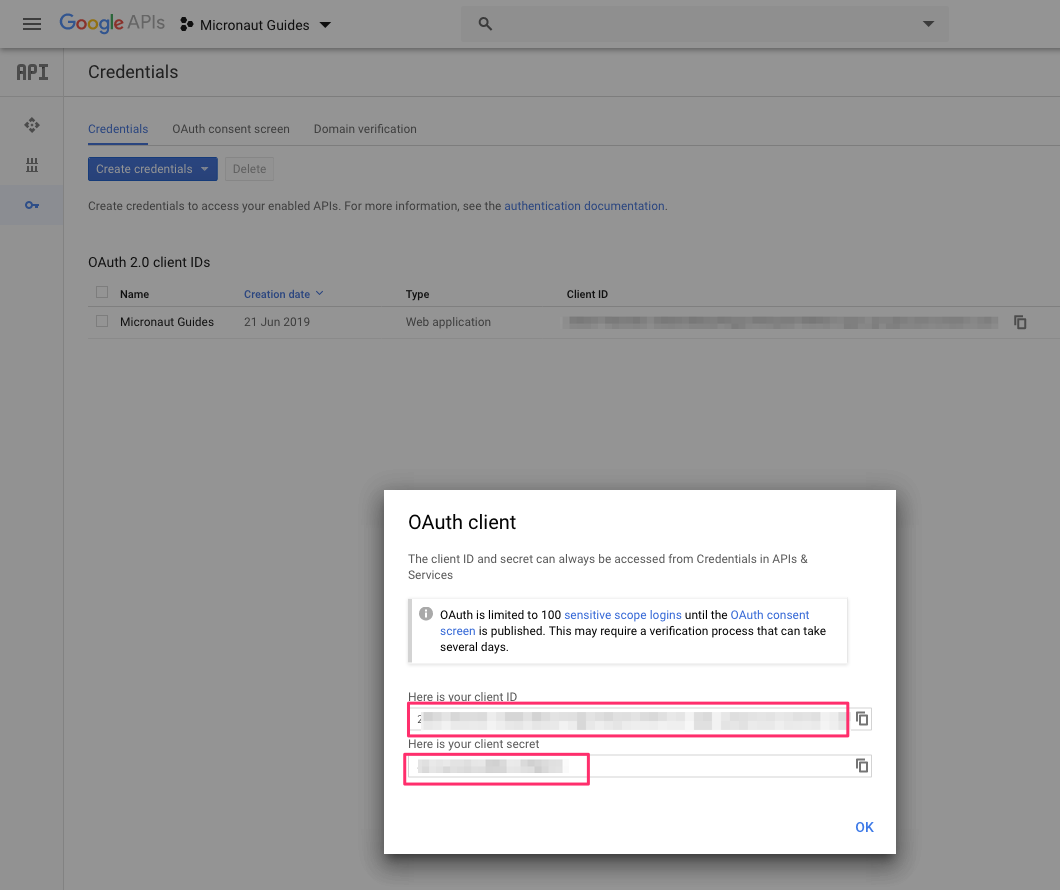
You will then receive a client ID and secret.
To use OAuth 2.0 integration in your Micronaut application, add the following dependency:
implementation("io.micronaut.security:micronaut-security-oauth2")Also add Micronaut JWT support dependencies:
implementation("io.micronaut.security:micronaut-security-jwt")Add the following OAuth2 Configuration:
---
micronaut:
security:
authentication: idtoken (1)
oauth2:
clients:
google: (2)
client-id: '${OAUTH_CLIENT_ID:xxx}' (3)
client-secret: '${OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET:yyy}' (4)
openid:
issuer: 'https://accounts.google.com' (5)
endpoints:
logout:
get-allowed: true (6)| 1 | Set micronaut.security.authentication as idtoken. The idtoken provided by Google when the OAuth 2.0 Authorization code flow ends will be saved in a cookie. The id token is a signed JWT. For every request, the Micronaut framework extracts the JWT from the Cookie and validates the JWT signature with the remote Json Web Key Set exposed by Google. JWKS is exposed by the jws-uri entry of Google .well-known/openid-configuration. |
| 2 | You can choose any name. The name you select, will be used in your routes. E.g. If you set google the login route for this OAuth 2.0 client is /oauth/login/google |
| 3 | Client Secret. See previous screenshot. |
| 4 | Client ID. See previous screenshot. |
| 5 | issuer URL. It allows the Micronaut framework to discover the configuration of the OpenID Connect server. |
| 6 | Accept GET request to the /logout endpoint. |
The previous configuration uses several placeholders. You will need to set up OAUTH_CLIENT_ID, OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET environment variables.
export OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=XXXXXXXXXX export OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=YYYYYYYYYY
Check Google .well-known/openid-configuration documentation.
We want to use an Authorization Code grant type flow which it is described in the following diagram:
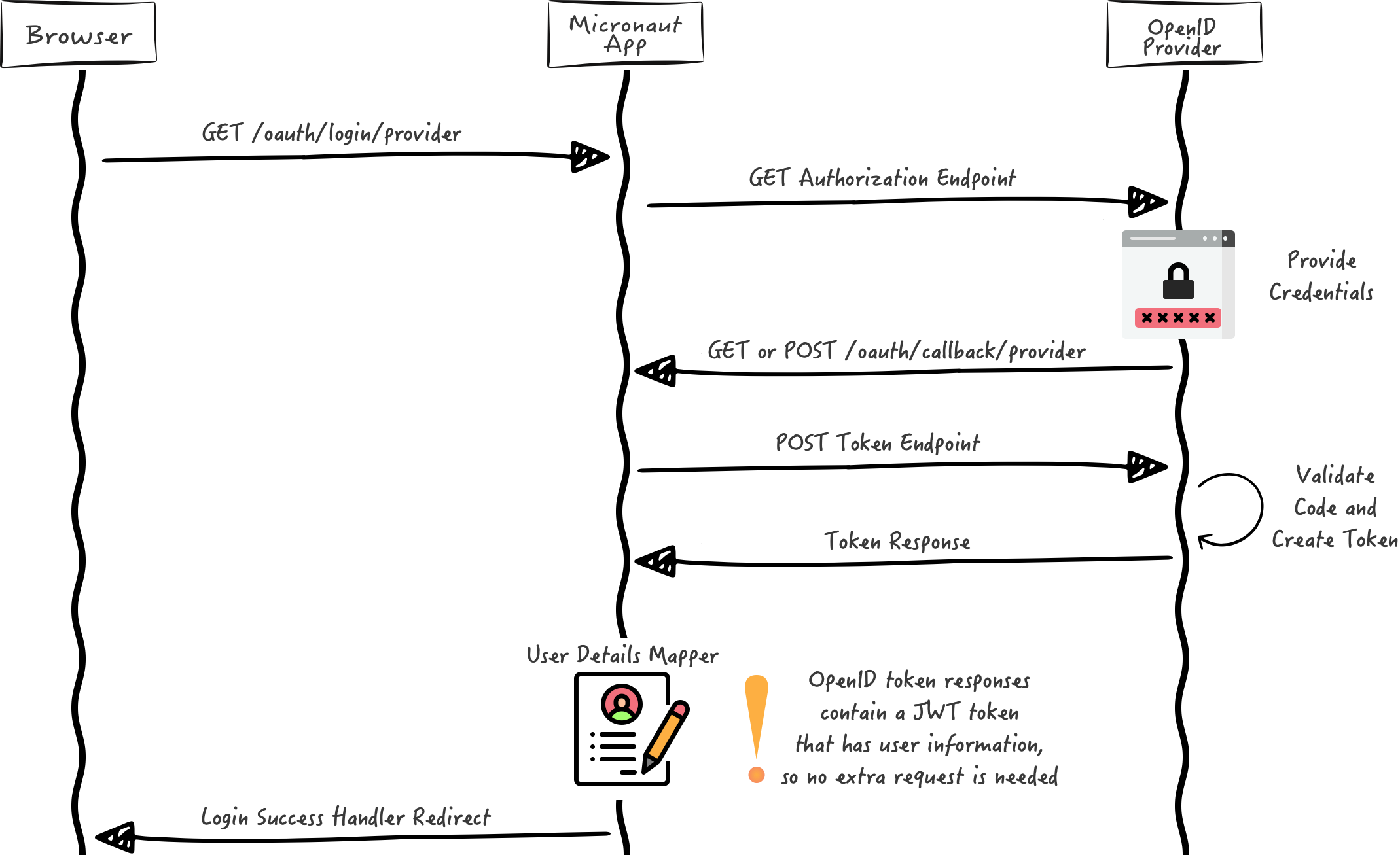
4.3. Home
Create a controller to handle the requests to /. You will display the email of the authenticated person if any. Annotate the controller endpoint with @View since we will use a Thymeleaf template.
package example.micronaut
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Controller
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Get
import io.micronaut.security.annotation.Secured
import io.micronaut.security.rules.SecurityRule
import io.micronaut.views.View
@Controller (1)
class HomeController {
@Secured(SecurityRule.IS_ANONYMOUS) (2)
@View("home") (3)
@Get (4)
fun index(): Map<String, Any> = HashMap()
}| 1 | The class is defined as a controller with the @Controller annotation mapped to the path /. |
| 2 | Annotate with io.micronaut.security.Secured to configure secured access. The SecurityRule.IS_ANONYMOUS expression will allow access without authentication. |
| 3 | Use View annotation to specify which template to use to render the response. |
| 4 | The @Get annotation maps the index method to GET / requests. |
Create a thymeleaf template:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Micronaut - Google example</h1>
<h2 th:if="${security}">username: <span th:text="${security.attributes.get('email')}"></span></h2>
<h2 th:unless="${security}">username: Anonymous</h2>
<nav>
<ul>
<li th:unless="${security}"><a href="/oauth/login/google">Enter</a></li>
<li th:if="${security}"><a href="/logout">Logout</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</body>
</html>Also, note that we return an empty model in the controller. However, we are accessing security in the thymeleaf template.
-
The SecurityViewModelProcessor injects into the model a
securitymap with the authenticated user. See User in a view documentation.
5. Running the Application
To run the application, use the ./gradlew run command, which starts the application on port 8080.
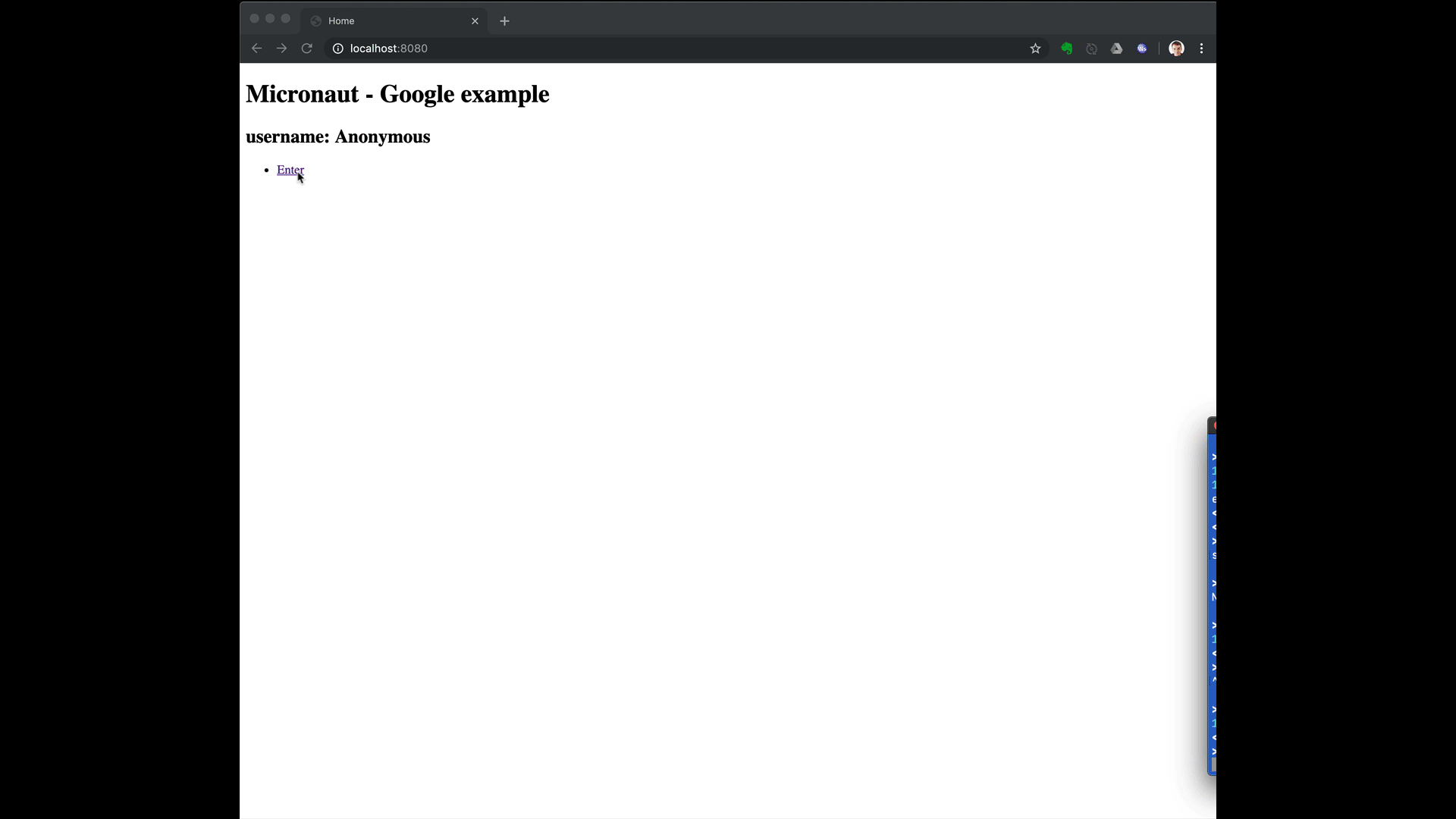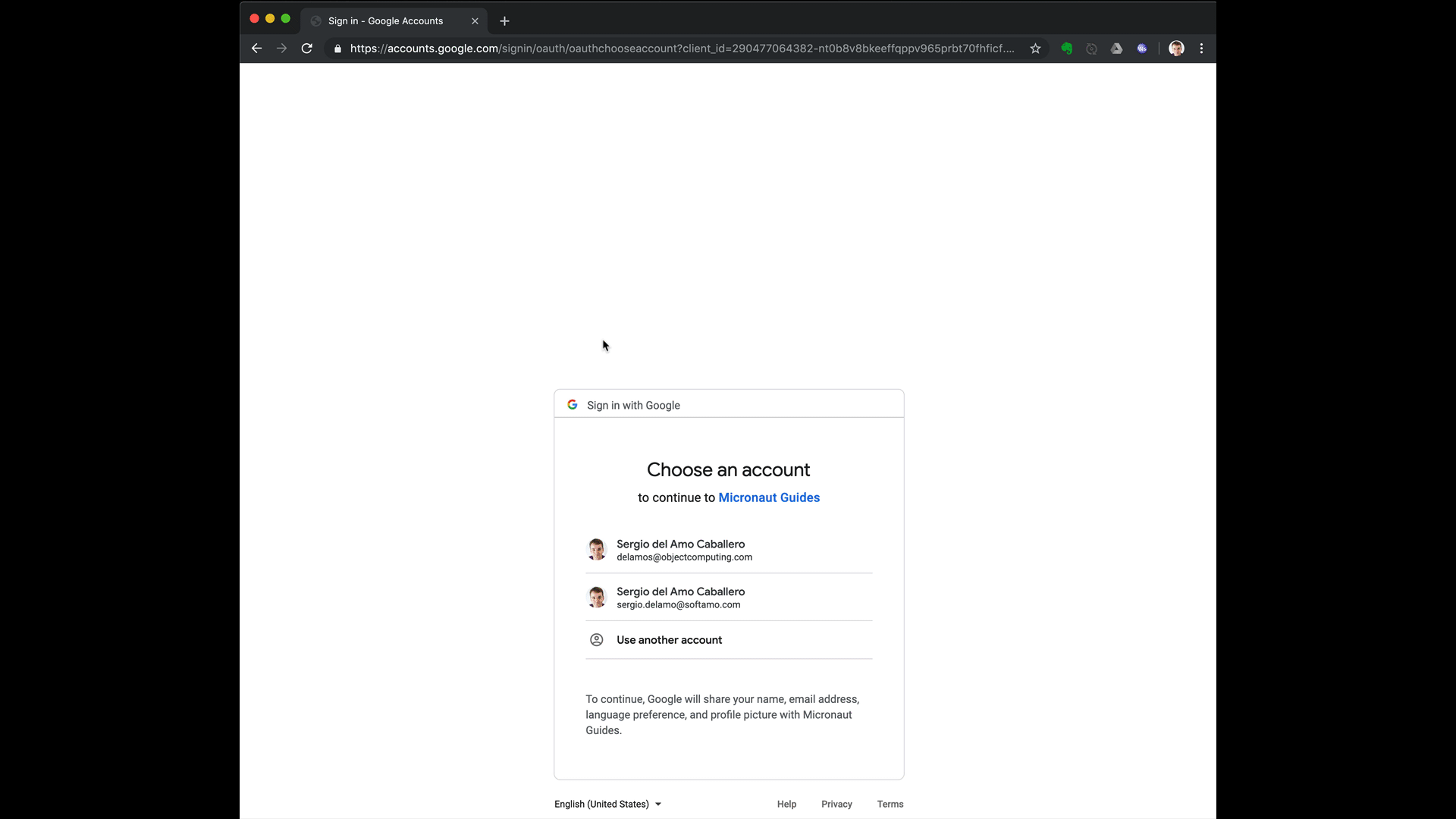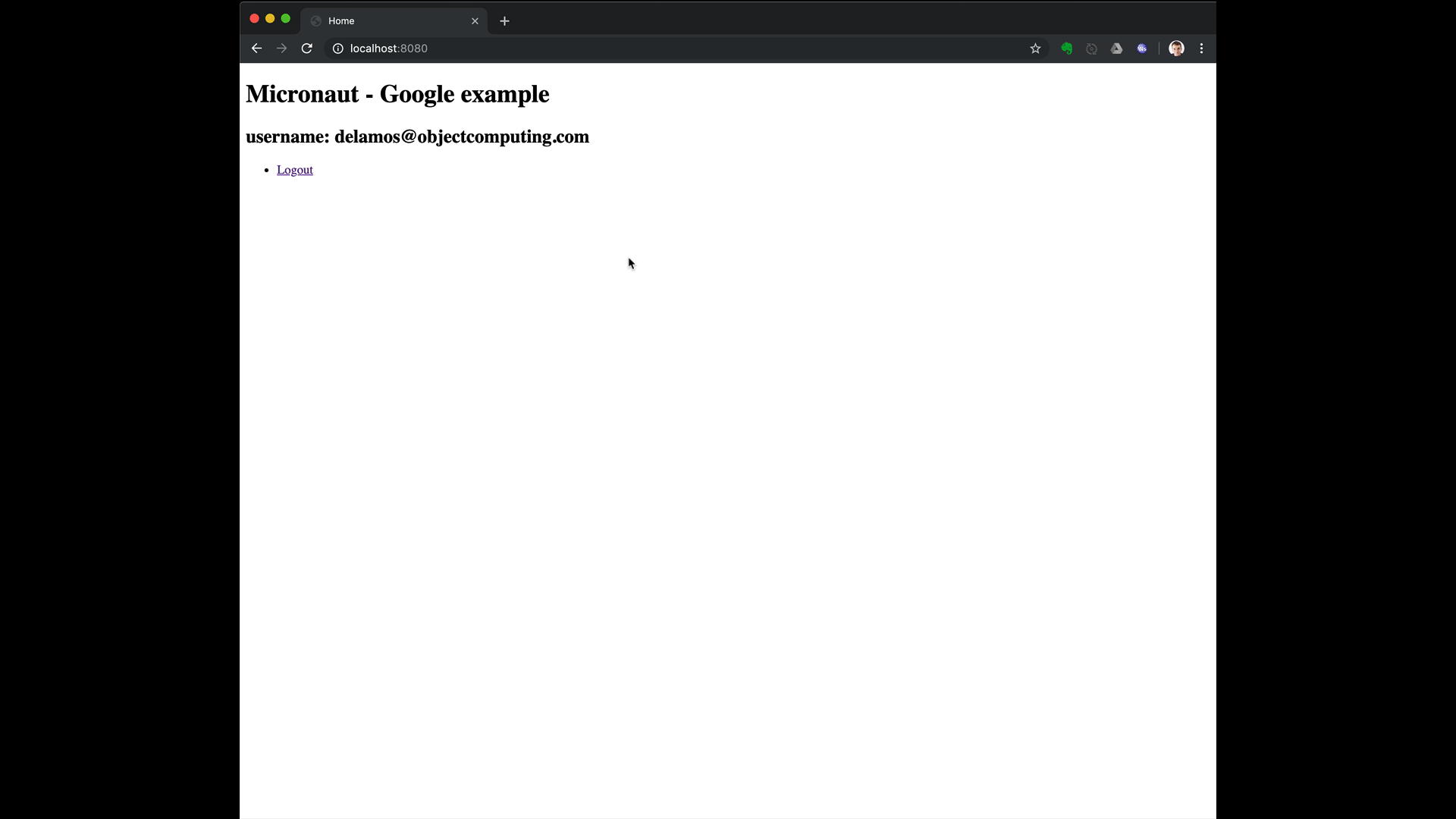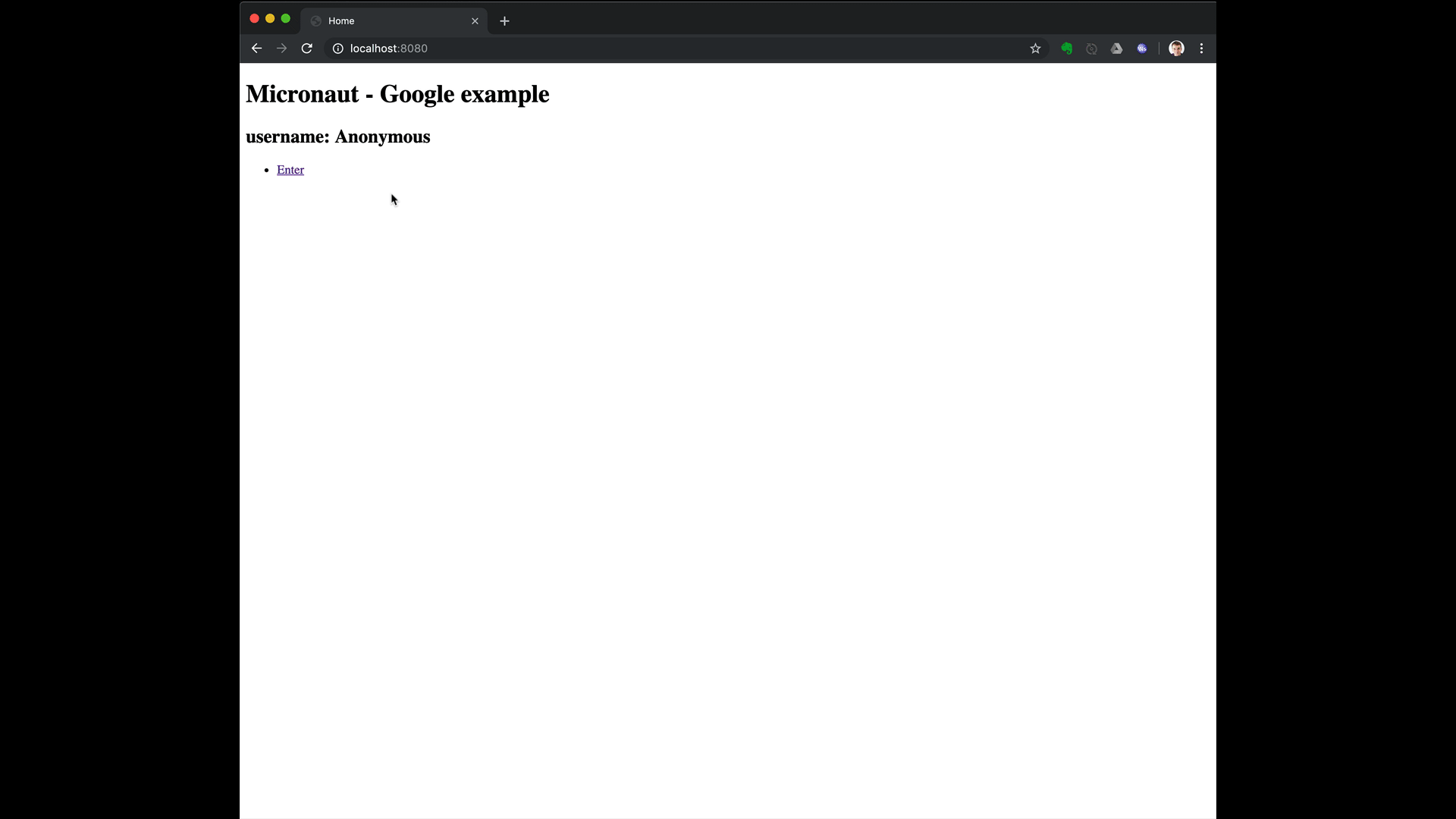
5.1. Custom ID token claims validation
Imagine you want to allow sign-in with Google but only to users' in your organization.
Google OAuth consent screen settings allows you to do that:
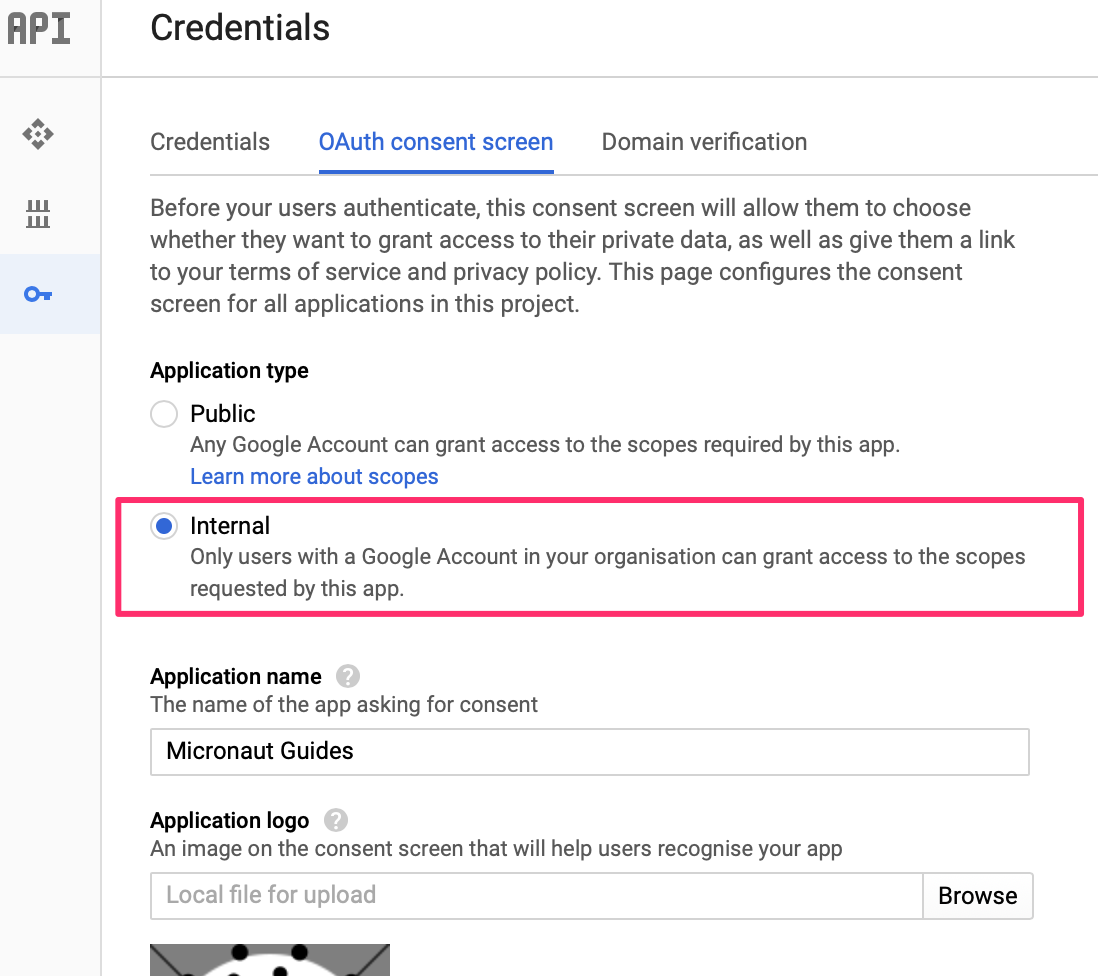
However, we could also achieve this programmatically. Google id token contains a claim named hd which stands for hosted domain.
We can create a configuration object:
package example.micronaut
interface ApplicationConfiguration {
val hostedDomain: String
}Backed by a @ConfigurationProperties annotated class:
package example.micronaut
import io.micronaut.context.annotation.ConfigurationProperties
import io.micronaut.context.annotation.Requires
@Requires(property = "app.hosted-domain")
@ConfigurationProperties("app")
class ApplicationConfigurationProperties : ApplicationConfiguration {
override lateinit var hostedDomain: String
}and then implement a OpenIdClaimsValidator bean. The Micronaut framework validates the id token against every bean of type OpenIdClaimsValidator. If the id token hd claim does not match the value configured, it is considered invalid.
package example.micronaut
import io.micronaut.context.annotation.Requires
import io.micronaut.security.oauth2.client.OpenIdProviderMetadata
import io.micronaut.security.oauth2.configuration.OauthClientConfiguration
import io.micronaut.security.oauth2.endpoint.token.response.OpenIdClaims
import io.micronaut.security.oauth2.endpoint.token.response.validation.OpenIdClaimsValidator
import jakarta.inject.Singleton
@Requires(beans = [ApplicationConfiguration::class])
@Singleton
class HostedDomainClaimValidator(applicationConfiguration: ApplicationConfiguration) : OpenIdClaimsValidator {
private val hostedDomain: String
init {
hostedDomain = applicationConfiguration.hostedDomain
}
override fun validate(claims: OpenIdClaims,
clientConfiguration: OauthClientConfiguration,
providerMetadata: OpenIdProviderMetadata): Boolean {
val hd = claims[HOSTED_DOMAIN_CLAIM]
return hd is String && hd.equals(hostedDomain, ignoreCase = true)
}
companion object {
const val HOSTED_DOMAIN_CLAIM = "hd"
}
}Add to src/main/resources/application.yaml
app:
hosted-domain: 'objectcomputing.com'if you start the application, you will only be able to sign in with a Google Account within the OCI organization.
6. Generate a Micronaut Application Native Executable with GraalVM
We will use GraalVM, the polyglot embeddable virtual machine, to generate a native executable of our Micronaut application.
Compiling native executables ahead of time with GraalVM improves startup time and reduces the memory footprint of JVM-based applications.
Only Java and Kotlin projects support using GraalVM’s native-image tool. Groovy relies heavily on reflection, which is only partially supported by GraalVM.
|
6.1. Native executable generation
The easiest way to install GraalVM on Linux or Mac is to use SDKMan.io.
sdk install java 22.3.r11-grl| If you still use Java 8, use the JDK11 version of GraalVM. |
sdk install java 22.3.r17-grlFor installation on Windows, or for manual installation on Linux or Mac, see the GraalVM Getting Started documentation.
After installing GraalVM, install the native-image component, which is not installed by default:
gu install native-imageTo generate a native executable using Gradle, run:
./gradlew nativeCompileThe native executable is created in build/native/nativeCompile directory and can be run with build/native/nativeCompile/micronautguide.
It is possible to customize the name of the native executable or pass additional parameters to GraalVM:
graalvmNative {
binaries {
main {
imageName.set('mn-graalvm-application') (1)
buildArgs.add('--verbose') (2)
}
}
}| 1 | The native executable name will now be mn-graalvm-application |
| 2 | It is possible to pass extra arguments to build the native executable |
After you execute the native executable, navigate to localhost:8080 and authenticate with Google.
7. Next steps
Read Micronaut OAuth 2.0 documentation to learn more.
8. Help with the Micronaut Framework
The Micronaut Foundation sponsored the creation of this Guide. A variety of consulting and support services are available.