mn create-app example.micronaut.micronautguide --build=maven --lang=groovyTable of Contents
Distributed Configuration with AWS Secrets Manager and the Micronaut Framework
Learn how to load your secrets from AWS Secrets Manager in your Micronaut application
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 3.9.2
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Groovy.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE
-
JDK 1.8 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
4. Writing the Application
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
If you don’t specify the --build argument, Gradle is used as the build tool. If you don’t specify the --lang argument, Java is used as the language.
|
The previous command creates a Micronaut application with the default package example.micronaut in a directory named micronautguide.
5. OAuth 2.0 Dependency
To use OAuth 2.0 integration, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.security</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-security-oauth2</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>6. Micronaut AWS Secrets Manager Dependency
Add the following dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.aws</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-aws-secretsmanager</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.aws</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-aws-sdk-v2</artifactId>
<version>@micronaut-aws-sdk-v2Version@</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>7. Distributed Configuration
7.1. Enable Distributed Configuration
Create a bootstrap.yml file in the resources directory to enable distributed configuration.
Add the following:
| 1 | Set the application name in bootstrap.yml instead of application.yml so that it is available when reading configuration from distributed sources.
properties |
| 2 | Set microanut.config-client.enabled: true which is used to read and resolve configuration from distributed sources. |
7.2. Clean up Application Configuration
If application.yml sets micronaut.application.name, remove it. You moved it to bootstrap.yml.
- micronaut:
- application:
- name: micronautguide7.3. Disable Distributed Configuration for Test
To disable distributed configuration for tests, create a bootstrap-test.yml file:
micronaut:
config-client:
enabled: false8. Create Secret
OAuth 2.0 clients have a client id and secret property. We will save both in AWS Secrets Manager.
Create a Secret in AWS Secrets Manager
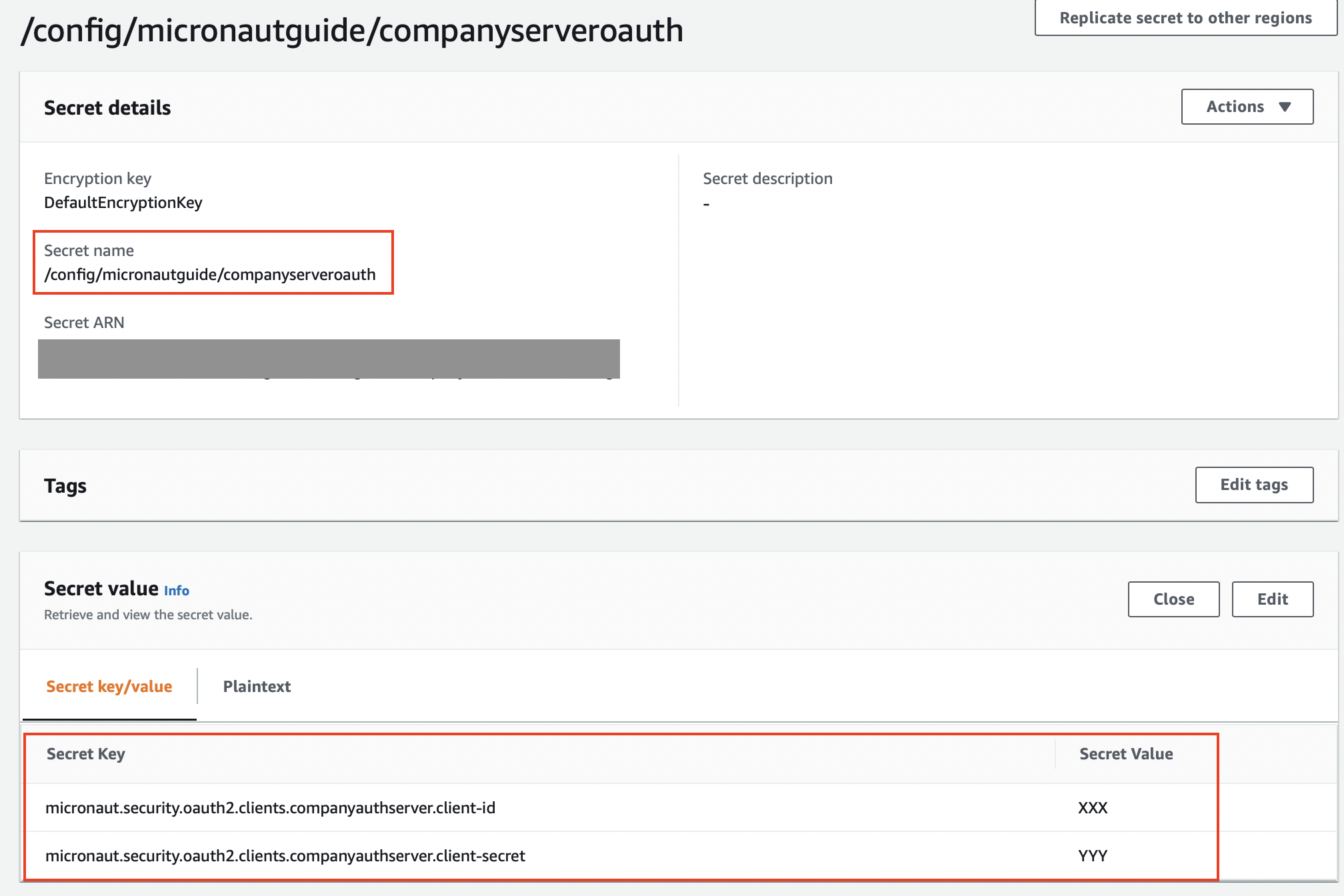
9. Controller
Create a controller which exposes the value read from AWS Secrets Manager.
package example.micronaut
import io.micronaut.http.MediaType
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Controller
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Get
import io.micronaut.http.annotation.Produces
import io.micronaut.security.annotation.Secured
import io.micronaut.security.oauth2.configuration.OauthClientConfiguration
import io.micronaut.security.rules.SecurityRule
import jakarta.inject.Named
@Controller
class ClientIdController {
private final OauthClientConfiguration oauthClientConfiguration;
ClientIdController(@Named("companyauthserver") OauthClientConfiguration oauthClientConfiguration) {
this.oauthClientConfiguration = oauthClientConfiguration
}
@Secured(SecurityRule.IS_ANONYMOUS)
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
@Get
String index() {
oauthClientConfiguration.clientId
}
}10. Logs
Add the following configuration to src/main/resources/logback.xml to get a more verbose output when the application starts up:
<logger name="io.micronaut.aws.distributedconfiguration" level="TRACE"/>11. Running the Application
To run the application, use the ./mvnw mn:run command, which starts the application on port 8080.
You should see traces such as:
12:26:56.602 [main] INFO i.m.context.DefaultBeanContext - Reading Startup environment from bootstrap.yml
12:26:57.554 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - application name: micronautguide
12:26:59.266 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - evaluating 2 keys
12:26:59.267 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - adding property micronaut.security.oauth2.clients.companyauthserver.client-id from prefix /config/micronautguide/
12:26:59.268 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - adding property micronaut.security.oauth2.clients.companyauthserver.client-secret from prefix /config/micronautguide/
12:26:59.268 [main] DEBUG i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - Property source awssecretsmanager with #2 items
12:26:59.268 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - property micronaut.security.oauth2.clients.companyauthserver.client-id resolved
12:26:59.268 [main] TRACE i.m.a.d.AwsDistributedConfigurationClient - property micronaut.security.oauth2.clients.companyauthserver.client-secret resolved
12:26:59.319 [main] INFO i.m.d.c.c.DistributedPropertySourceLocator - Resolved 1 configuration sources from client: compositeConfigurationClient(AWS Secrets Manager)
12:26:59.767 [main] INFO io.micronaut.runtime.Micronaut - Startup completed in 3378mscurl localhost:8080XXXX12. Next steps
Explore more features with Micronaut Guides.
Learn more about Micronaut AWS Secrets Manager integration.
Read about AWS Secrets Manager
13. Help with the Micronaut Framework
The Micronaut Foundation sponsored the creation of this Guide. A variety of consulting and support services are available.